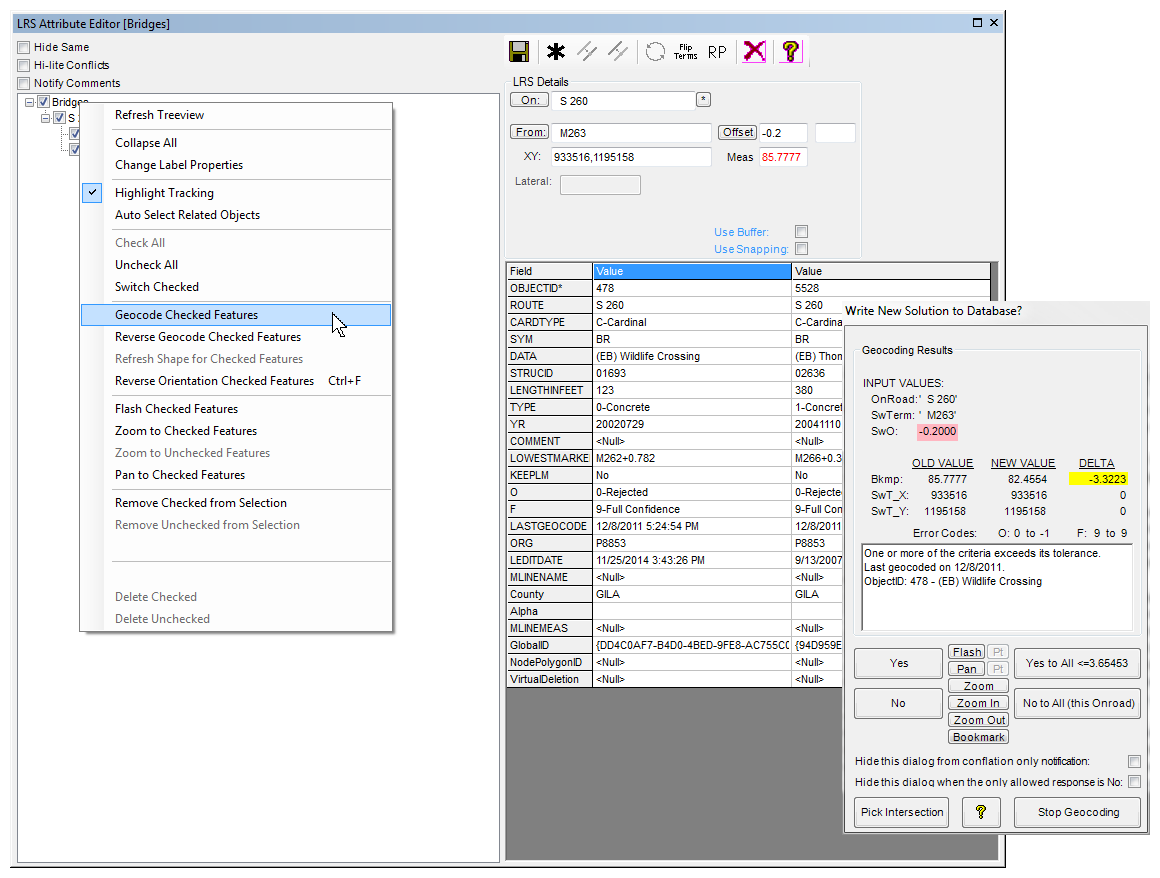
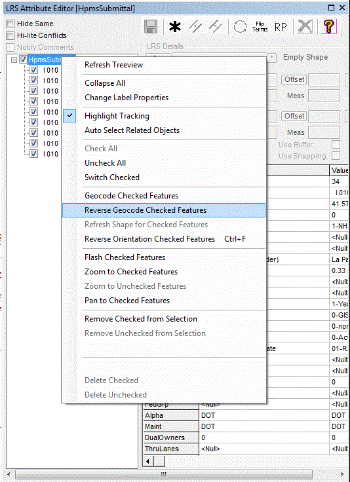
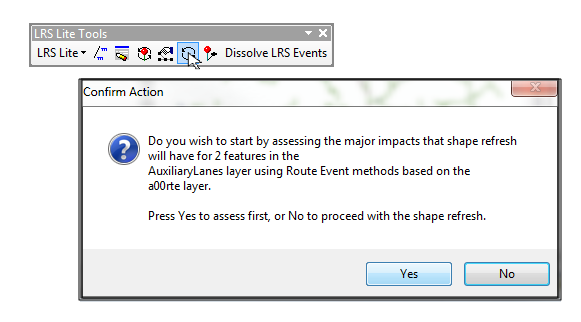
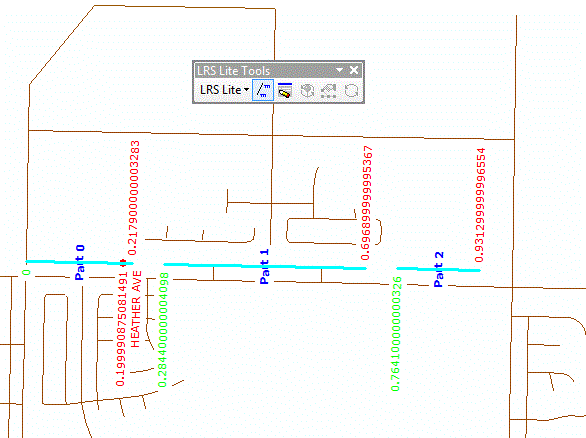
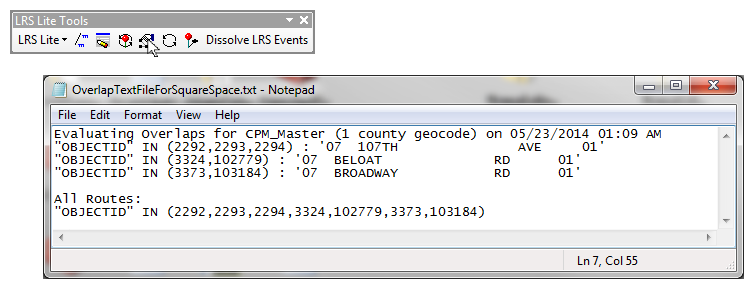
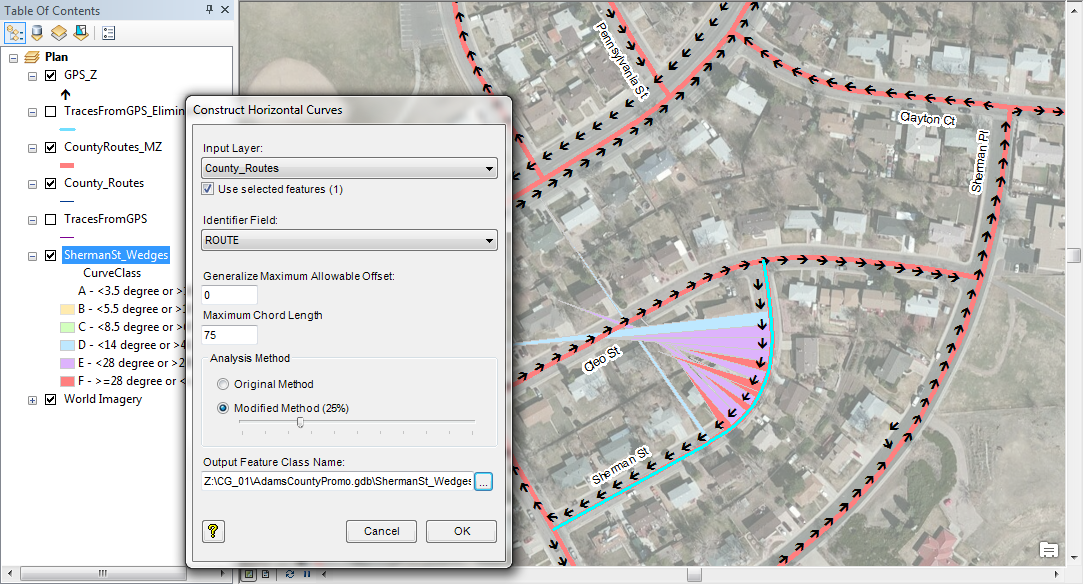
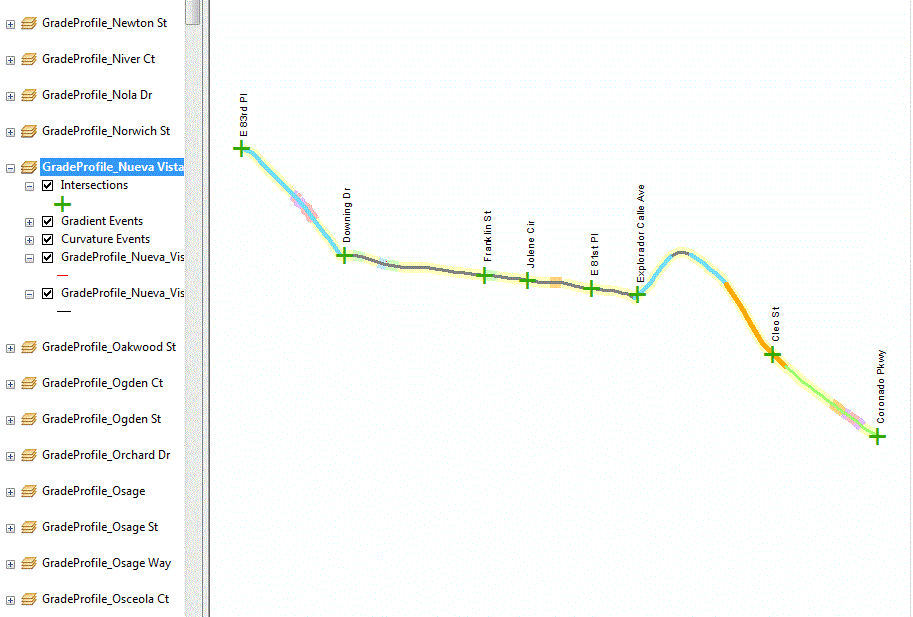
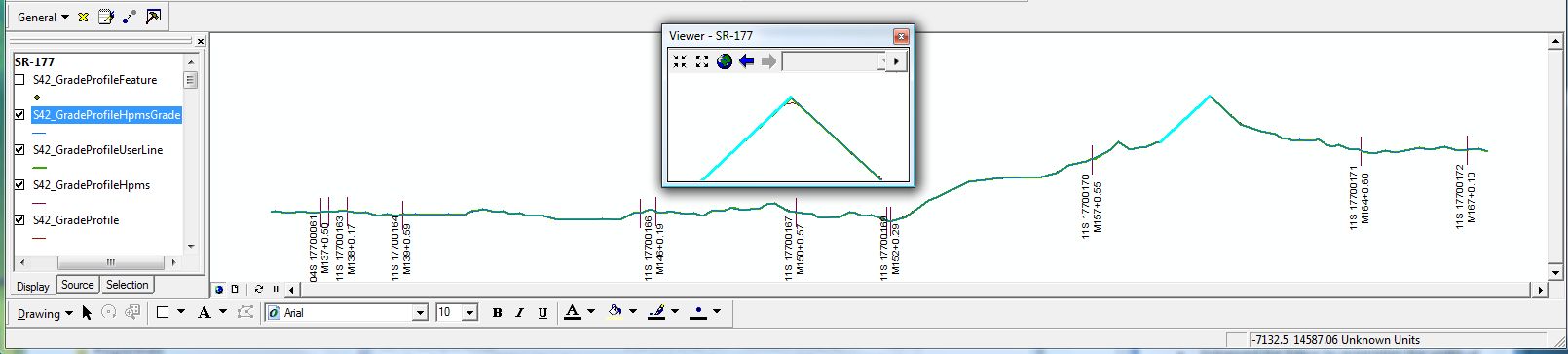
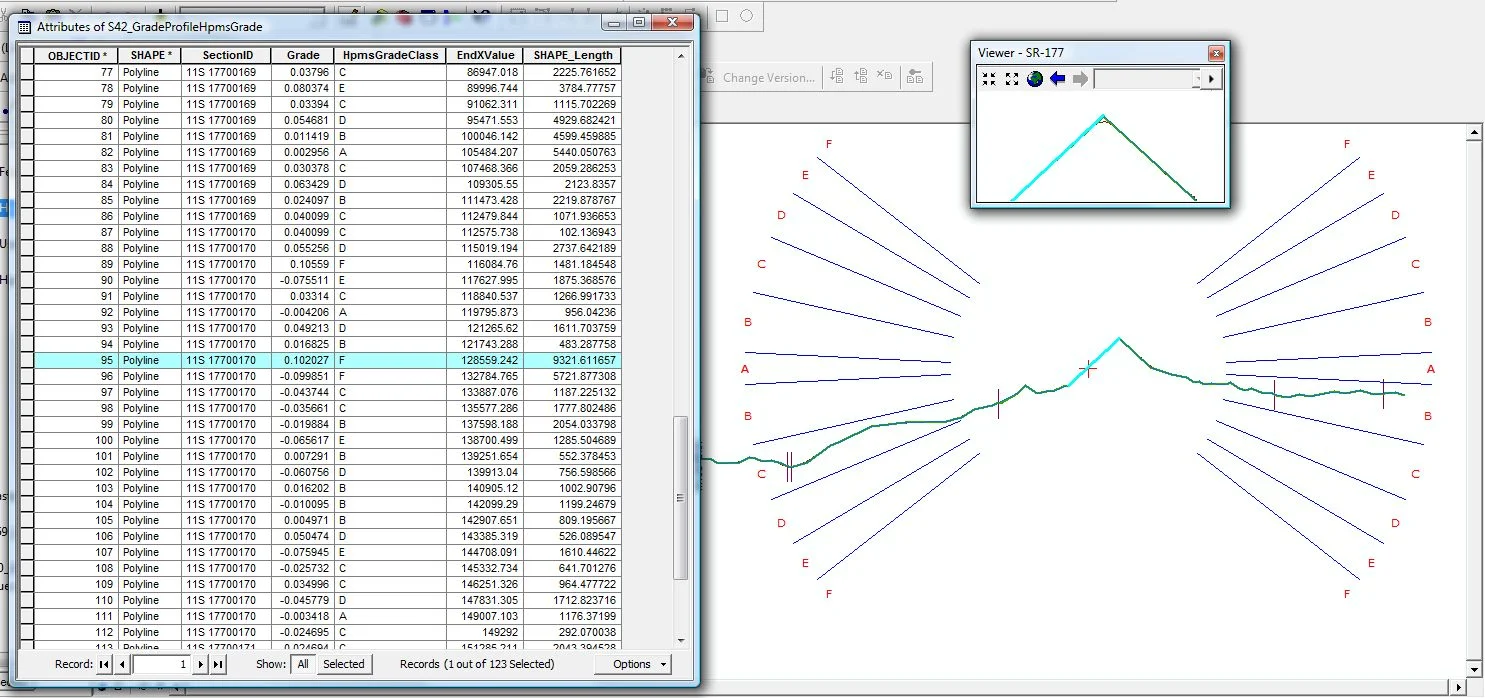
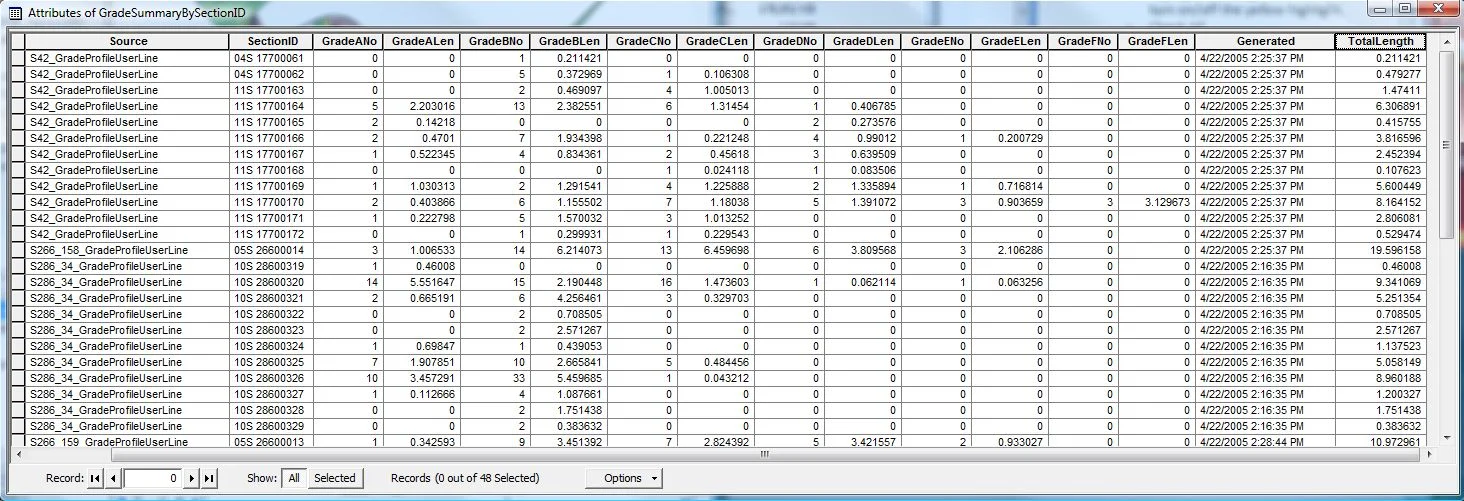
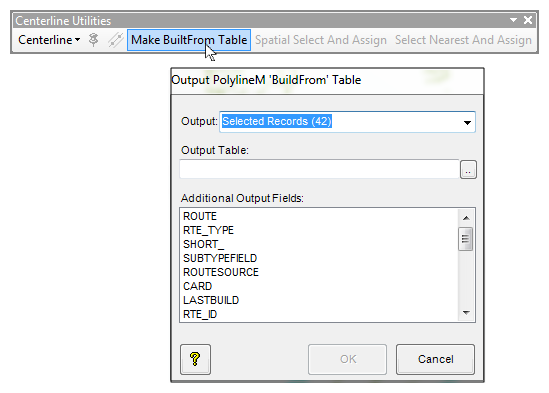
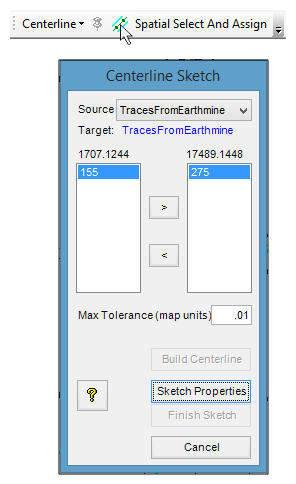
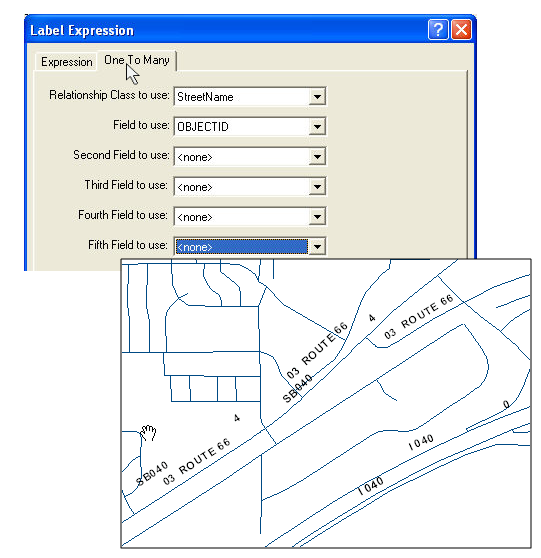
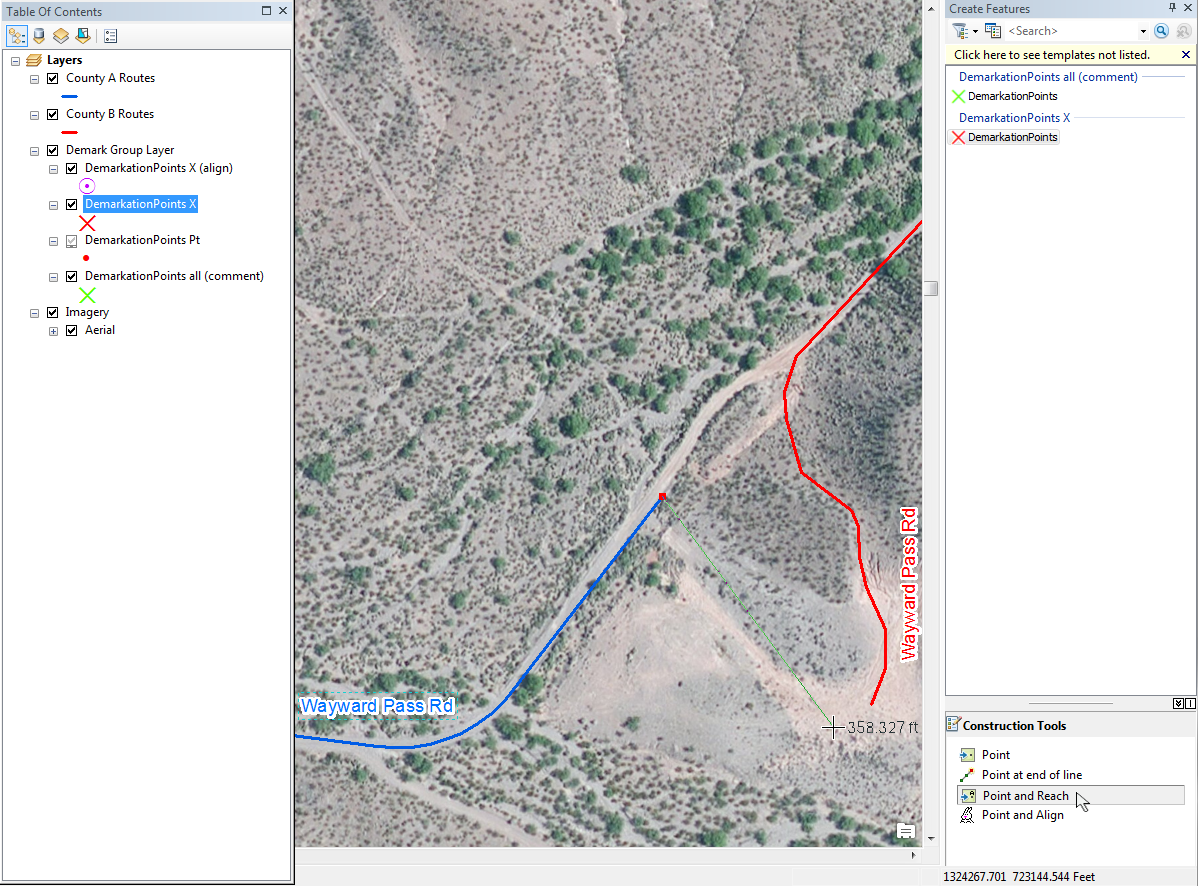
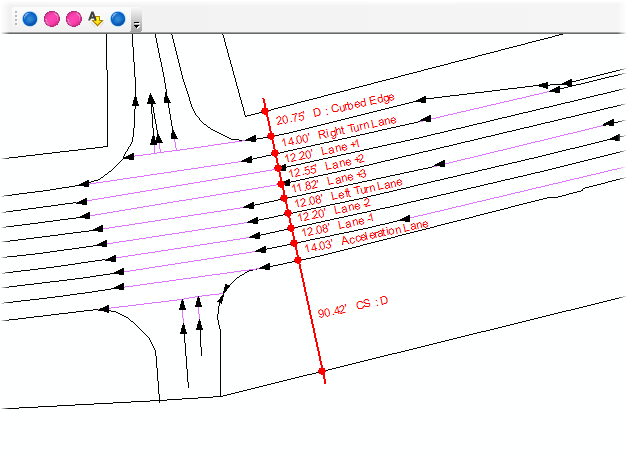
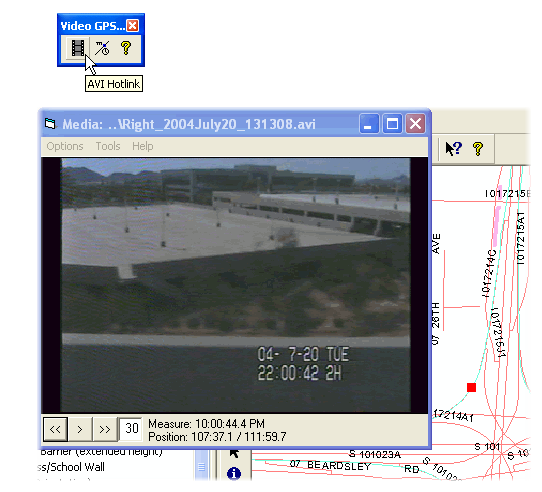
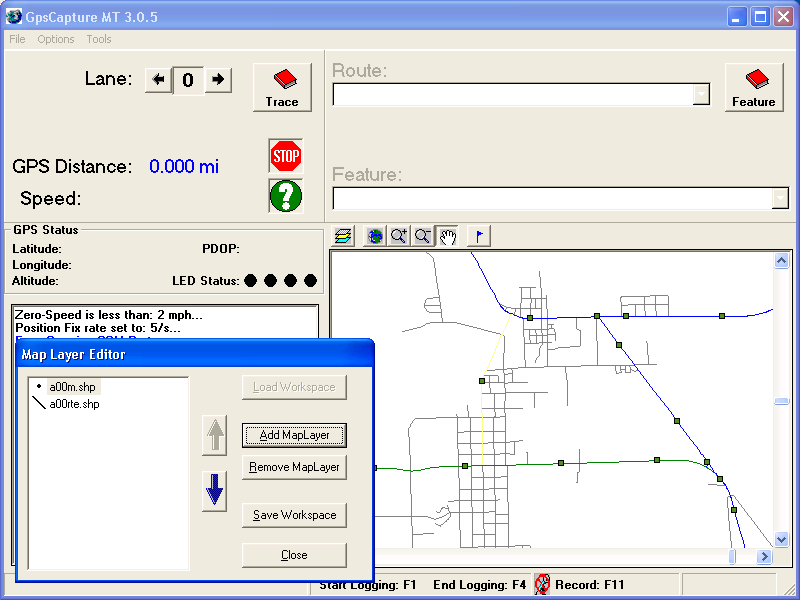
Are you a fan of Geoprocessing Tools? Within ModelBuilder or elsewhere in the ArcGIS workspace? Many of our landmark methods are available for integration into your workflows using our custom Python scripts and .Net geoprocessing tools.
LRS Utilities Toolset
Add Virtual Markers to LRS Tables More...
Assign Nearest More...
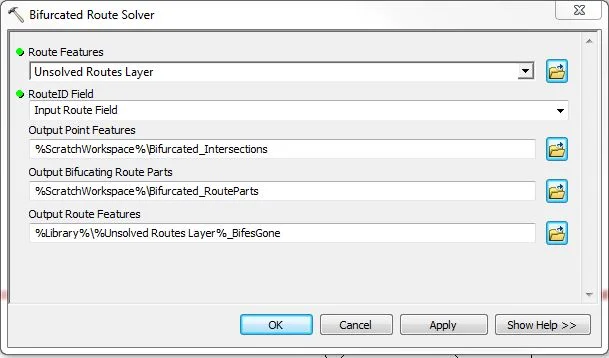
Bifurcated Route Solver More...
Calculate LRS Measure Fields More...
Calculate LRS Measure from XY Fields More...
Calculate Nearest Marker Field More...
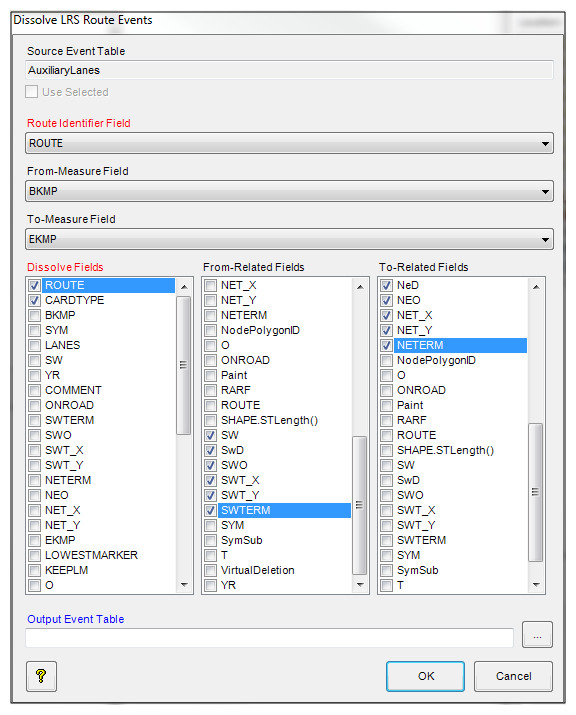
Dissolve LRS Features More...
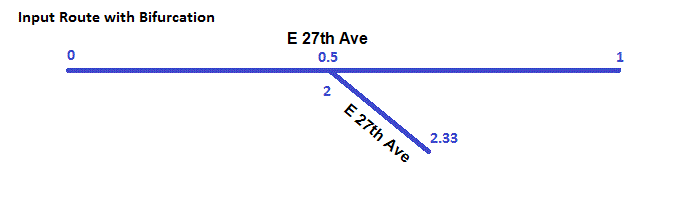
Flag Bifurcating Polyline Features More...
Four-table Route Builder More...
Make Finite LRS Events More...
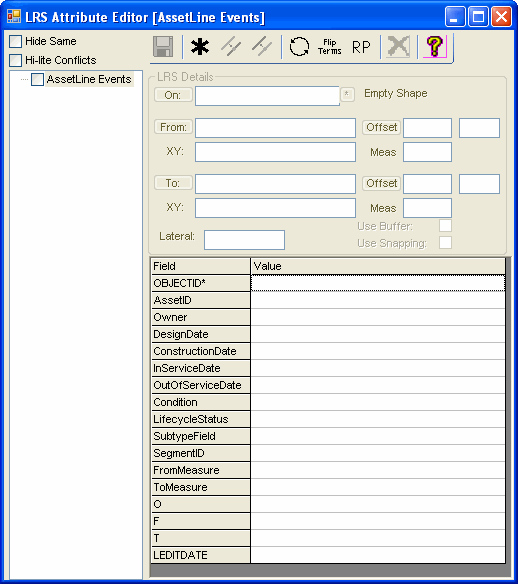
Redact LRS Events More...
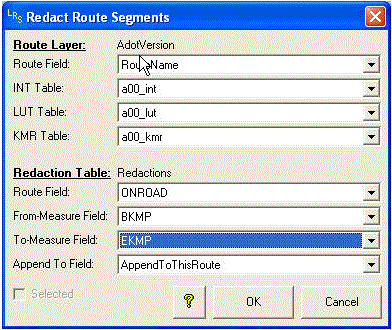
Redact Routes More...
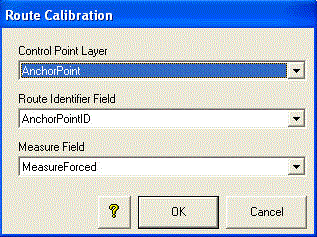
ReOrient And Measure Routes More...
Select by LRS Reference More...
EditTracker Utilities Toolset
Apply EditTracker Extension More...
Enable or Disable EditTracker Extension More...
Remove EditTracker Extension More...
Geoprocessing Utilities Toolset
Factor Measures More...
Insert Vertices More...
Interpolate/Extrapolate Z-Coordinates More...
Retrace Partial Polylines More...
Line-Based Inventory Toolset
Add Features to Connect Proximal Features More...
Intersect Line-based Polygons w/ LRS Events More...
At-Large Tools
Make Line Events From Point Events More...
Break Range into Bins of Max Range Value More...
Export Table to Delimited File More...
Sample Panel - Stats by Vol Group More…
Increment/Decrement More…